Unveiling the secrets of cell division, the Amoeba Sisters Mitosis Answer Key provides a comprehensive guide to the intricacies of mitosis, a fundamental process that underpins life’s growth and renewal. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of cell biology, where the Amoeba Sisters’ engaging video serves as our guide.
From the initial stages of prophase to the final stages of telophase, we’ll explore the key events that characterize each phase of mitosis, unraveling the intricate dance of chromosomes as they align, divide, and migrate to opposite poles of the cell.
Along the way, we’ll dispel common misconceptions and clarify the role of mitosis in maintaining genetic stability.
Amoeba Sisters Mitosis Overview: Amoeba Sisters Mitosis Answer Key
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells. It is essential for growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms.
The Amoeba Sisters video on mitosis provides a clear and concise overview of the process. It covers the key stages of mitosis, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, and explains the role of each stage in ensuring the accurate duplication and distribution of genetic material.
Key Concepts of Mitosis
- Mitosis is a continuous process, but it is traditionally divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- During prophase, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- In metaphase, the chromosomes align at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase is the stage during which the sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase is the final stage of mitosis, during which the chromosomes decondense, the nuclear envelope reforms, and the cell divides into two daughter cells.
Stages of Mitosis
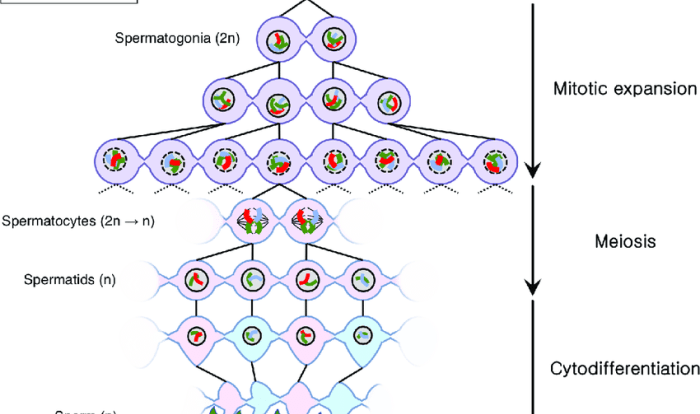
Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells from a single parent cell. It occurs in four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
| Stage | Key Events |
|---|---|
| Prophase |
|
| Metaphase |
|
| Anaphase |
|
| Telophase |
|
Importance of Mitosis
Mitosis plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
During growth, mitosis allows organisms to increase their size and complexity by generating new cells. This process is essential for the development of multicellular organisms from a single fertilized egg.
Repair, Amoeba sisters mitosis answer key
Mitosis also contributes to tissue repair. When cells are damaged or die, mitosis produces new cells to replace them. This process ensures that tissues and organs can maintain their function and integrity.
Asexual Reproduction
In some organisms, mitosis is the sole means of reproduction. This process, known as asexual reproduction, produces genetically identical offspring. Mitosis ensures that the genetic material of the parent organism is passed on to the offspring without any alterations.
Moreover, mitosis plays a vital role in maintaining genetic stability. During cell division, the chromosomes are duplicated and then distributed equally to the daughter cells. This process ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material, preserving the genetic integrity of the organism.
Misconceptions and Clarifications
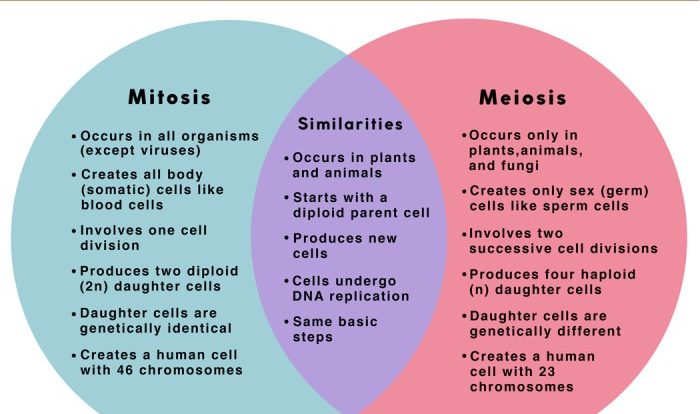
Mitosis is a complex process, and there are some common misconceptions about it. One of the most common misconceptions is that mitosis is the same as meiosis. While mitosis and meiosis are both cell division processes, they are actually quite different.
Mitosis is a process that results in two identical daughter cells. These daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis, on the other hand, is a process that results in four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Meiosis is also a more complex process than mitosis, and it involves two rounds of cell division.
Another common misconception about mitosis is that it is only important for growth and development.
While mitosis is essential for growth and development, it is also important for other processes, such as tissue repair and replacement. For example, when you cut your skin, the cells in the area around the cut will divide by mitosis to repair the damaged tissue.
Additional Resources
To delve deeper into the intricacies of mitosis, explore the following resources:
Relevant Websites, Articles, and Videos
Amoeba Sisters Resources
- Amoeba Sisters: Mitosis Overview
- Amoeba Sisters: Stages of Mitosis
- Amoeba Sisters: Importance of Mitosis
- Amoeba Sisters: Misconceptions and Clarifications about Mitosis
FAQ Compilation
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells, ensuring the accurate transmission of genetic material during cell division.
Why is mitosis important?
Mitosis plays a crucial role in growth, repair, and asexual reproduction, enabling the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms.
What are the key stages of mitosis?
Mitosis consists of four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, each characterized by specific events in chromosome behavior.