Welcome to the fascinating world of cell division! Dive into the cell division crossword answer key, a treasure trove of knowledge that will unravel the intricacies of mitosis and meiosis. From understanding the significance of cell division in biological processes to unraveling the role of chromosomes and genetic recombination, this guide will illuminate the wonders of cellular reproduction.
Prepare to embark on a journey through the stages of mitosis, where chromosomes dance and spindle fibers guide the division of cells. Uncover the secrets of meiosis, where genetic diversity takes center stage. With this answer key as your compass, navigate the complexities of cell division and unlock the mysteries of cellular reproduction.
Cell Division Overview
Cell division is a fundamental process in biology that ensures the growth, repair, and reproduction of organisms. It involves the division of a single cell into two or more daughter cells.
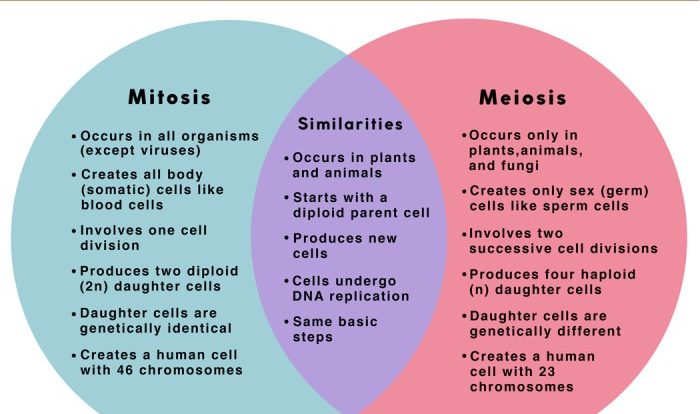
There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is responsible for the growth and repair of tissues, while meiosis is involved in sexual reproduction.
Stages of Mitosis
Mitosis occurs in four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. In anaphase, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
In telophase, two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell divides into two daughter cells.
Stages of Meiosis
Meiosis occurs in two rounds of division, known as meiosis I and meiosis II. In meiosis I, the chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. The chromosomes then separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
In meiosis II, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. The result of meiosis is four haploid cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells from a single parent cell. It is a continuous process, but for the sake of understanding, it is divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Chromosomes
During prophase, the chromatin in the nucleus condenses into visible chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids, which are identical copies of each other.
Spindle Fibers
As the chromosomes condense, the spindle fibers form in the cytoplasm. The spindle fibers are made up of microtubules, which are long, thin protein filaments. The spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes at the centromere, which is the narrow region of the chromosome where the sister chromatids are joined.
Cell Cycle
Mitosis is part of the cell cycle, which is the process by which cells grow and divide. The cell cycle is divided into four phases: G1, S, G2, and M. Mitosis occurs during the M phase of the cell cycle.
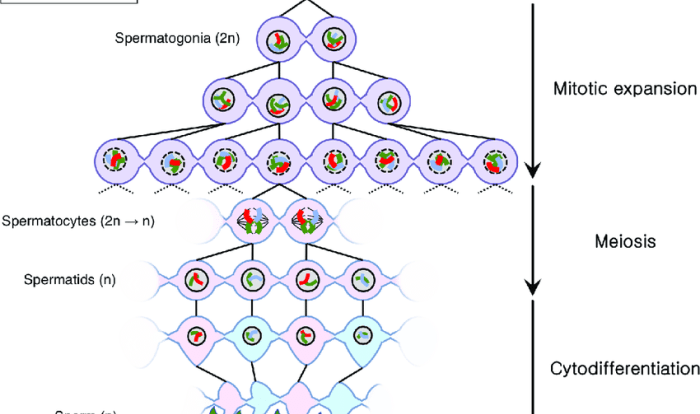
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing gametes (sex cells) with a haploid number of chromosomes. Unlike mitosis, meiosis involves two rounds of division, resulting in four daughter cells with distinct genetic compositions.
Meiosis plays a crucial role in sexual reproduction, ensuring genetic diversity among offspring. It shuffles the genetic material through a process called genetic recombination, leading to the creation of unique gametes that carry a combination of both parental chromosomes.
Stages of Meiosis
Meiosis I
- Prophase I:Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing-over. This process creates new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes.
- Metaphase I:Homologous chromosome pairs line up at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase I:Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I:Two daughter cells are formed, each with a haploid number of chromosomes.
Meiosis II
- Prophase II:Chromosomes condense again.
- Metaphase II:Chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase II:Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II:Four daughter cells are formed, each with a haploid number of chromosomes.
Genetic Recombination in Meiosis
Genetic recombination is a key feature of meiosis that shuffles the genetic material and creates new combinations of alleles. During prophase I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing-over. This process results in the formation of recombinant chromosomes that carry a combination of both parental chromosomes.
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes ensures that each gamete carries a unique combination of alleles, increasing genetic diversity among offspring.
Crossword Answer Key: Cell Division Crossword Answer Key
To solve the crossword puzzle, refer to the clues provided and fill in the corresponding squares with the correct answers. The answer key below will guide you in completing the puzzle accurately.
The crossword puzzle is designed to reinforce your understanding of key concepts related to cell division. By solving the puzzle, you can assess your knowledge and identify areas where further review may be beneficial.
Across
- A type of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells (5 letters): MITOSIS
- The stage of mitosis where chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell (7 letters): METAPHASE
- The structure that separates chromosomes during cell division (6 letters): SPINDLE
- A type of cell division that produces four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell (6 letters): MEIOSIS
Down, Cell division crossword answer key
- The stage of mitosis where the nuclear envelope breaks down (6 letters): PROPHASE
- The stage of mitosis where chromosomes become visible (7 letters): PROMETAPHASE
- The stage of mitosis where chromosomes are pulled apart (6 letters): ANAPHASE
- The stage of mitosis where daughter cells are formed (6 letters): TELOPHASE
Answers to Common Questions
What is the significance of cell division?
Cell division is crucial for growth, development, tissue repair, and reproduction in all living organisms.
What are the key differences between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse daughter cells.
What is the role of chromosomes in cell division?
Chromosomes carry genetic material and are duplicated and separated during cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.